Articles
What’s Next for CAR Cell Therapy?
February 2024
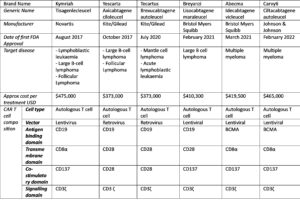
The first generation CAR T cell was discovered in 1993 when the variable region of an antibody was fused to the constant regions of a T cell receptor. Now, 20 years later, the global CAR T cell therapy market is worth approximately $8.44 billion and is expected to hit around $88.5 billion by 2032.
Scientific progress within the cancer immunotherapy field has led to the following six CAR-T cell therapy approvals by the FDA and EMA, along with other regulatory agencies.
Given the success of these CAR T cell treatments, what is next for CAR T cell therapy and what is being done to make these treatments more readily available?
CAR Natural Killer cells
The most prominent toxicity of CAR T cells is known as cytokine release syndrome (CRS). CRS is caused by abundant pro-inflammatory cytokine release from target and immune effector cells. One of the approaches taken to tackle this issue is CAR-NK cell therapy. Unlike CAR T cells which can release pro-inflammatory cytokines, NK cells have a different spectrum of secreted cytokines, that are considered safer than those induced by CAR T cells. There are currently 39 published clinical trials recruiting patients for CAR-NK cell therapy.
Allogeneic CAR T cells
As reflected in their price tag, another limitation of CAR T cell therapy is the cost and time taken for manufacturing these products. The current FDA approved CAR T cells are generated from patient cells, known as autologous T cells. Not only is this process of generating CAR T cells time consuming and costly, often the patient’s T cells are depleted due to them already receiving chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. In contrast, using T cells obtained from healthy donors (allogeneic T cells) provides high, functional amounts of cells, allowing for “off-the -shelf” CAR T cell products. There are currently 33 published clinical trials recruiting patients for allogeneic CAR T cell therapy.
Controllable CAR cells
Another issue facing current CAR T cell therapies is T cell exhaustion. T cell exhaustion is caused by excessive antigen signalling, resulting in a prolonged excessive immune response that leaves CAR T cells exhausted before they can eliminate tumours. As such, limiting or interrupting CAR:antigen interaction is an attractive strategy for ameliorating exhaustion in CAR T cells. To counteract CAR T cell exhaustion, adapter mediated CARs have been developed. With adapter mediated CAR systems, the CAR T cell does not bind directly to the tumour antigen. Instead, the CAR T cell binds to an adaptor and the adaptor binds to the tumour antigen. Adapter molecules are subsequently administered to patients and act as a linker between the tumour and CAR T cell, effectively turning the CAR T cell on. By effectively controlling CAR T cell function, CAR T cell activity can be regulated even once administered to a patient, allowing for a more safe and effective treatment.
Beyond cancer
At present, CAR T cell therapy has only been approved for use in certain cancers. Fuelled by the unprecedented 90% remission rate shown by most of the approved CAR-T cell therapies, there are over 600 ongoing CAR-T clinical trials focusing on a range of cancer treatments. However, CAR cell therapy is not limited to cancer treatment. Recent clinical studies using CAR T cells to treat HIV have demonstrated safe and successful results. CAR cell therapy has also shown remarkable results in fibrotic diseases such as cardiac fibrosis.
In conclusion, CAR cell therapy continues to make significant progress, and whilst there are still several challenges that need to be overcome, the future of CAR cell therapy holds exciting potential.